5 Ways to Maximize Ecommerce Profit Margins
Our independent research projects and impartial reviews are funded in part by affiliate commissions, at no extra cost to our readers. Learn more
We all want to make more profit – right?
It’s what drives us to work hard and be innovative with our online stores. It’s what makes us seek out new ways to sell more and make more. In all likelihood, it’s what has brought you here to read this article.
Below, we have outlined five of the very best ways to boost your ecommerce profit margins when selling online. So read on and discover how to start making more profit today!
What Is a Profit Margin?
Your profit margin is the money you are left with after making a sale. Profit can be calculated in a few different ways – here are a few common types:
Gross Profit
This is the profit left after deducting the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS).
Gross Profit = Revenue – COGS
For example, if you sold a delicious apple pie for $5 and the ingredients to make that apple pie cost you $2, then your gross profit margin is $3.
Gross profit doesn’t account for overheads, taxes, or other costs.
Operating Profit
Operating profit starts with gross profit and then removes additional expenses such as overhead costs. It also accounts for depreciation and amortization.
Operating Profit = Revenue – COGS – Overhead Costs – Depreciation and Amortization
For example, if you sold an apple pie for $5 and it cost you:
- $2 in ingredients
- $1.50 in overheads (energy, employee wages)
- $0 in depreciation and amortization
Then your operating profit would be $1.50 on each pie sold.
Operating profit doesn’t account for taxes.
Net Profit
Your net profit is what you are left with after deducting all costs associated with making a sale including COGS, taxes, overhead costs, depreciation, and amortization.
Net Profit = Revenue – COGS – Overhead Costs – Depreciation and Amortization – Taxes
Let’s use our pie example from above. If your operating profit was $1.50 and you had to pay 20% on that profit ($0.30) then your net profit would be $1.20 on each pie sold.
Typically net profit is your true profit, since it is what you are physically left with after all costs have been applied.
In this article, we will typically focus our advice on helping ecommerce businesses maximize their gross and operating profit margins – this is because we won’t be offering any advice on how to lower the amount of tax you pay.
What Is a Good Profit Margin for Ecommerce?
This may seem like a silly question. Surely we should aim for the highest ecommerce profit margin possible, right?
Well no, this isn’t actually ecommerce best practice.
It is beneficial to take a realistic approach to your ecommerce margins since it gives realistic targets to work towards.
In addition to this, even if you are successful in creating a very high-profit margin within your niche, this leaves you open to competition following the same processes but providing the same products at a much lower price in exchange for lower profits – potentially threatening your business.
So, what should your target profit margin be? Unfortunately, there’s no simple answer to the question “what is a good profit margin for ecommerce?” But as a rule of thumb:
- 5% is considered low
- 10% is considered average
- 20% is considered very good
However, in reality, it is impossible to give a single percentage that ecommerce businesses should work towards.
This is because all businesses differ in how they’re run and differ even more between niches. A healthy profit margin for a business that sells a niche, technical product is likely to be very different to that of an ecommerce store that sells a product in a highly competitive market.
Volumes also come into play. A business may decide to sell at a lower profit margin in order to capture a larger market share and increase its volume of sales. Whereas another business may decide to serve a small, specialist market, but increase their profit margin to cover the fact that they sell a low volume of products. These two businesses would have very different profit margin percentages and sales volumes but could have very similar actual profits at the end of the year.
5 Ways to Maximize Your Ecommerce Profit Margin
#1. Increase Prices
Increasing your prices is probably the most obvious way to boost your profit margins. It is simple math – increase your price per unit, but keep your cost per unit the same and you will immediately see an increased margin.
However, increasing prices can also be daunting…
What if people aren’t willing to pay the new price? You could use valuable customers.
One good strategy to increase prices is to do it in line with inflation. This will be largely expected by most consumers. This approach won’t necessarily increase your profit margin percentage because the cost of purchase is also likely to go up at the same rate. However, it will make the original profit margin percentage worth more in actual cash value.
Let’s use an online surf store as an example:
Wetsuit before inflation:
- $50 cost
- $100 sale
- 50% profit margin
- Actual profit $50
Wetsuit after 20% inflation:
- $60 cost
- $120 sale
- Same 50% profit margin
- Actual profit $60 ($10 increase)
Another strategy is to increase prices slowly over time and carefully monitor demand. When you find that the price increase is making customers move elsewhere, stop the increases.

#2. Lower Unit Purchase Costs
Another simple, yet effective way of increasing ecommerce profit margins is to lower the cost you pay per unit. For ecommerce websites this can typically be done in two ways:
- Negotiate lower costs with your current suppliers
- Find new, cheaper suppliers
#3. Lower Operating Costs
Operating costs are often overlooked when it comes to maximizing profit margins. Yet they can sometimes be the quickest and easiest way to do it.
While increasing prices requires you to convince customers to spend more and lowering unit purchase costs requires you to convince suppliers to sell to you for less – lowering operating costs can typically be done on your own terms.
How you lower operating costs will depend largely on where you are spending your money. Start by itemizing all your regular overhead costs and sorting them by largest to smallest. Work through and assess easy ways to minimize each.
For example, if your office space is one of your biggest overheads, ask yourself if you can move to cheaper offices or even adopt a work-from-home policy.
You can also lower operating costs by finding smart ways to streamline processes.
#4. Sell More
Ok, it might seem like we are pointing out the obvious here, but selling more is a crucial step in maximizing profit. This is especially true when you’ve already spent considerable time lowering your costs and you have pushed your prices to their limit.
Selling more will usually involve smart marketing campaigns. However, it is crucial to keep an eye on your return on investment (ROI) because increased marketing costs can eat into profits.
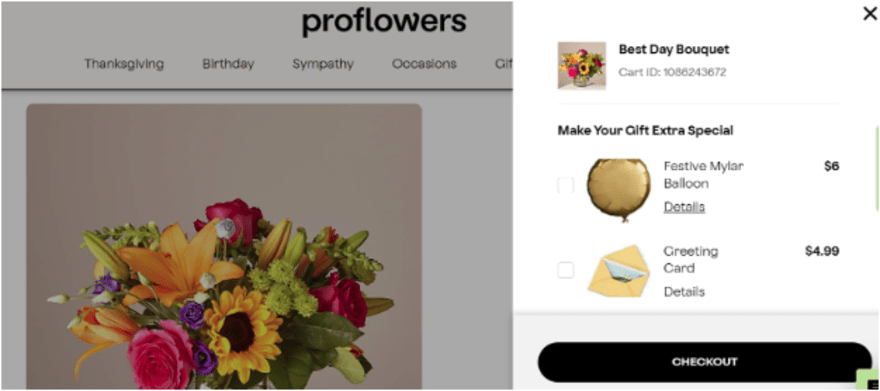
#5. Cross-Sell & Upsell
For businesses with a limited customer pool, selling more of the same items isn’t always an option. In these cases adding new, associated products to your store can help you take a cross-selling and upselling approach to increase sales and profit.
Find ways to sell customers products that either complement the products they already purchase from you, or alternatives that may do a better job at an increased cost.
Ecommerce Profit Margins: Summary
It’s clear that maximizing ecommerce profit margins is an essential part of continued ecommerce growth. In this guide, we have outlined some of the best ways to increase the percentage profit margin you make when selling online, as well as some ways to increase profit margins in actual cash value.
Leave a comment